Welcome to the first post in our new series on corrosion. Learn what corrosion is, how it affects the manufacturing process and the damage it can do if not monitored and addressed properly. Subscribe to our blog below so you don't miss any of our upcoming posts on this important topic!
Why You Should Care About Corrosion
Corrosion refers to a process that involves the deterioration or degradation of metal. It can cause a loss of efficiency and eventually a failure of equipment, leading to costly maintenance, downtime, and eventually the need for replacement. Nearly every company that uses water in any part of their process is affected by corrosion. The National Association of Corrosion Engineers' (NACE) Cost of Corrosion Study (1) shows that the estimated annual cost of corrosion in the U.S. is a staggering $276 billion—approximately 3.1% of our nation’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
What Causes Corrosion?
In the major water consuming industries like Pulp & Paper, Refining, Chemical and Power Plants, corrosion is often caused by three major sources - raw materials, the process itself and, most importantly, the water used during the manufacturing process. According to a recent NACE report (2), the water and wastewater sector alone accounts for approximately $36 billion or 14% of the estimated total corrosion cost mentioned above. The study revealed that, although corrosion management has improved over the past several decades, the U.S. must find more and better ways to encourage, support, and implement optimal corrosion control practices.
It is important to understand that corrosive ions in raw materials, such as chloride and sulfur in crude oil, or corrosive raw materials such as HF, sulfuric acid, caustic or chlorine can cause corrosion.
The production process itself and process conditions like high temperature and high pressure can also accelerate corrosion. For example, residual organically bound halide or sulfur compounds that are dormant under normal conditions become highly corrosive under high temperature and high-pressure process conditions, in which they release corrosive and toxic species.
Finally, corrosion is often caused by water used in the manufacturing process. Depending on the industry, the product type and the process condition, process water specifications vary widely and pose different corrosion-related challenges. For example, traces of chloride and sodium in process water are not problematic in refinery crude desalting or the pulp & paper bleaching process. However, traces of chloride and sodium cause irreversible damage to the wet process components of the steam generation process in power plants.
An integrated corrosion monitoring program is critical to achieve predictable plant operation and sustainable water use.
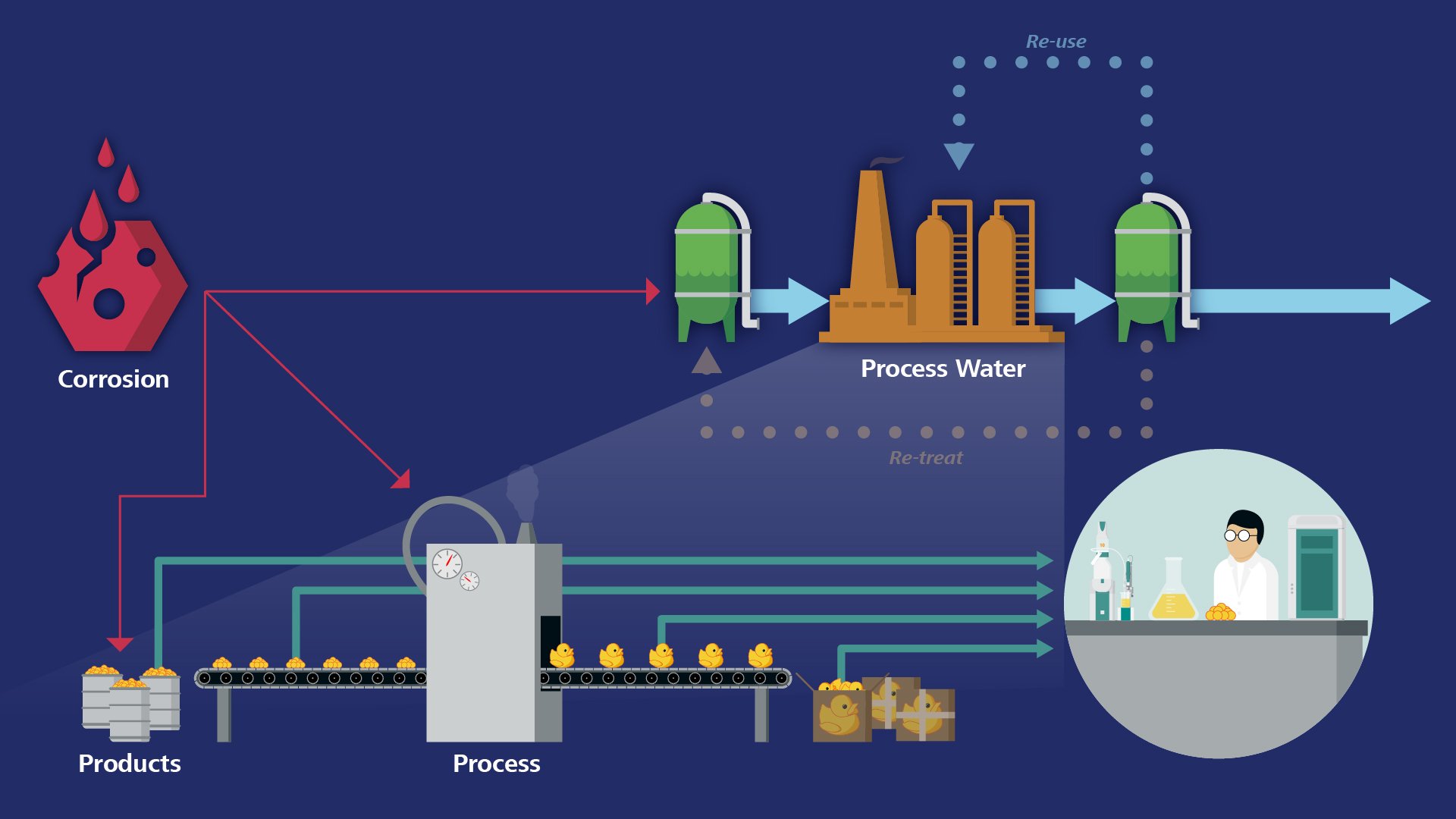
Why is Corrosion Especially Relevant in Process Water?
Boilers and cooling water systems are an integral part of process operations for major water consuming industries such as Pulp & Paper, Refining, Chemical and Power Plants. In these industries, corrosion issues are most significant for wet process equipment, such as boilers, heat exchangers, cooling water systems, and pipelines.
For steam generators, monitoring flow-accelerated corrosion (FAC) of the internal surfaces of the generator internals and other secondary system components is of utmost importance. FAC causes a degradation (loss of thickness) that leads to component fracture under operating conditions, which can jeopardize personnel safety. Microbiologically-induced corrosion (MIC), on the other hand, is a major concern for cooling water systems.
In addition to corrosion, scaling, which occurs in many process areas, is a common problem in manufacturing industries. For high plant productivity, process water requires suitable chemical treatment and a well-developed monitoring program.
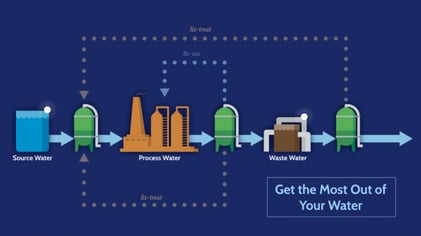 How Does Corrosion Monitoring Help You Get the Most Out of Your Water?
How Does Corrosion Monitoring Help You Get the Most Out of Your Water?
Corrosion monitoring is an important diagnostic tool and knowledge of the latest trends improves the effectiveness of your corrosion prevention plan. Testing and monitoring corrosives as raw materials and corrosive ions from raw materials not only helps maintain the quality of finished products, but also ensures overall plant performance and corrosion predictability.
Periodically analyzing corrosion products such as iron, chromium, and copper, helps identify early damage to the most expensive components and prevents unexpected shutdowns. The concentration of corrosion products indicates the effectiveness of the water treatment mechanisms used and are early indicators of failure. Identifying the right corrosion inhibitors suitable for the plant's metallurgy, followed by continual testing and monitoring, maintains effective plant operation and prevents corrosion and scaling.
No single test method will provide all the necessary data to properly evaluate the efficacy of corrosion and process water. A combination of selective techniques like Ion Chromatography, Voltammetry, Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS), or Titration, both in laboratory and process environments, gives you the information you need to combat corrosion and mitigates the risk of any unnecessary downtime.
Not having an efficient corrosion monitoring program costs companies billions of dollars each year. Don’t be one of them.
Stay tuned and subscribe below for the next update on corrosive ions testing.
References
(1) NACE International: https://www.nace.org/resources/general-resources/cost-of-corrosion-study
(2) NACE International: https://www.nace.org/resources/industries-nace-serves/water-wastewater
Posted by Metrohm USA Team
